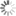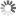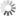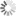Pompeii: Bathing Culture and the Development of Urban Space
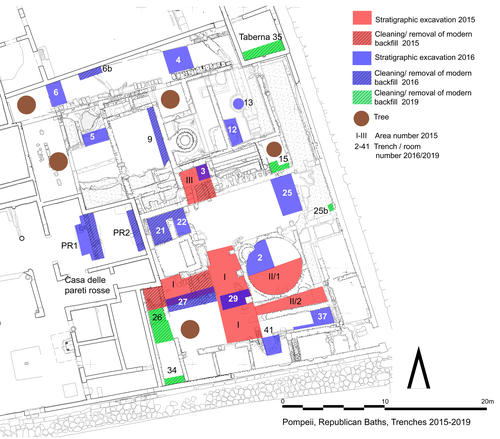
Fig. 1: Republican Baths: location of trenches
Bildquelle: FU Berlin
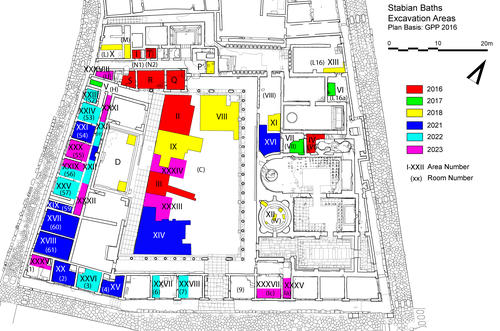
Fig. 2: Stabian Baths: location of trenches
Bildquelle: FU Berlin
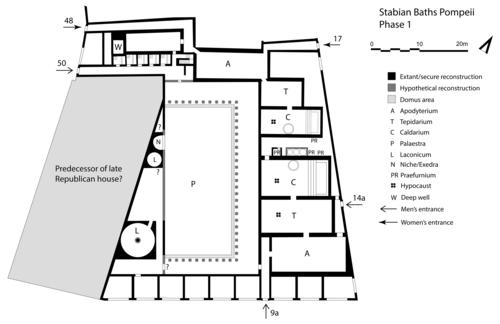
Fig. 3: Stabian Baths: reconstruction of the original baths, built after 130/120 BC
Bildquelle: FU Berlin
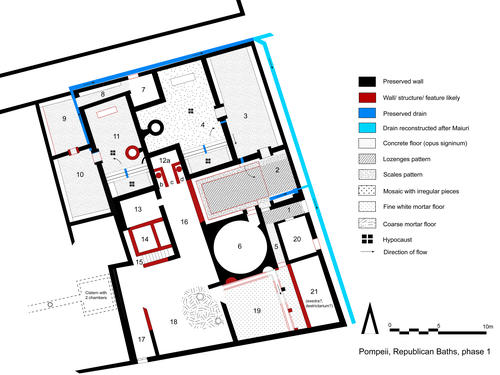
Fig. 4: Republican Baths: reconstruction of the original baths, built after 130/120 BC
Bildquelle: FU Berlin
Fig. 5: Stabian Baths, excavations in the palaestra, 2023
Bildquelle: Pompeji Projekt Berlin
GOAL
The development of a public collective bathing culture in Antiquity impacted directly on the formation of urban space and the socio-cultural function and perception of cities. The existence, location, accessibility, architectural context and infrastructure of public baths reflect changing standards and priorities of urban planning and lifestyle.
The first public baths (ca. 450 BC onwards) focused on individual bathing and cleansing aspects. In the Hellenistic period (3rd century BC onwards), there was a general trend towards more luxurious, innovative, collective, relaxing bathing forms. In the 2nd century BC, bathing programs were focused entirely on providing facilities for social and relaxing bathing. This final step required crucial innovations in technology and social concepts usually connected with Roman culture.
While the development of a specific Roman bathing culture in the Late Republican period currently is much debated, this topic is largely neglected in Pompeii, although the city includes three large baths dated to this period (Republican Baths, Stabian Baths, Forum Baths). This project examines the development, function, and cultural and sociohistorical context of the Republican Baths and Stabian Baths at Pompeii and their role in the urban development.
With its comprehensive reassessment of two key areas of Pompeii and its overarching focus on the multifaceted phenomenon of cityscaping, this project aims at contributing, beyond Pompeii and bathing culture, to current debates on the urbanization of Italy and the sociocultural, economic and political conditions, influences, and agents of this process.
FIELDWORK
Ten field seasons were carried out jointly with the University of Oxford (Mark Robinson) and since 2021 with the Università di Napoli L’Orientale (Marco Giglio); four seasons focused on the Republican Baths (fig. 1: 2015, 2016, 2019) and six focused on the Stabian Baths (fig. 2: 2016, 2017, 2018, 2021, 2022, 2023). Seasons comprised new stratigraphic excavations, investigations in archives and magazines, and detailed assessments of all standing remains, including the newest available 3D documentation and modelling techniques as well as traditional documentation methods.
This project was begun within the framework of the Excellence Cluster Topoi, group C-6 on “Cityscaping” and was generously funded by Topoi (2015–2018), by the Freie Universität (2019), and by the German Research Foundation (DFG, 2021–2023). Fieldwork on site was carried out with generous permission and support of the Parco Archeologico di Pompei with its directors Massimo Osanna and Gabriel Zuchtriegel.
RESULTS
The Stabian Baths are a key area for reconstructing the urban development of Pompeii and for studying the development of ancient bathing culture. According to Hans Eschebach (1979), the area was first occupied by an Archaic Altstadtmauer and from the 5th century BC onwards by a Greek palaestra with individual bathing cells that was gradually transforming, in five phases, into a Roman-type bath. Our excavations have shown that there is no trace of an early city wall at all, and that the Stabian Baths were only built after 130/120 BC and from the outset as Roman-type public bath (fig. 3). The complex was three times remodeled in line with major phases of Pompeii’s historical and urban development (after 80 BC, in the early 1st century AD, and after the major earthquake of AD 62). While the baths certainly functioned for some time after AD 62, further earthquake activity between AD 62 and the eruption of Vesuvius in AD 79 caused new damage. When Vesuvius erupted, the water supply did not work and thus the baths must have been closed.
The Republican Baths received little attention after their excavation and preliminary publication in 1950, although the area is central for the urban development of Pompeii. The project achieved two major goals: for the first time, the Republican Baths, have been fully documented and analyzed using both traditional and state of the art digital approaches. Second, the barely examined and debated construction date and history of the complex as well as the functioning of its technology (water management, heating system) could be clarified. The Republican Baths developed as a private complex after 130/120 BC (fig. 4) and underwent several changes, possibly after 80 BC to improve the technological standards and to meet new trends. While the Stabian Baths profited from the introduction of piped water into the city in the early Imperial period, the Republican Baths were abandoned around 30/20 BC and taken over by the owner of an adjacent house. The new owner used the terrain of the baths for a garden peristyle complex, which was once remodeled before it was significantly destroyed in the earthquake of AD 62. After this date, the terrain of the former baths was largely left in ruins and transformed into a building yard for quarrying volcanic ash and possibly for dumping building debris (fig. 3).
The project has shown that current understanding of the early phases of urban development in Pompeii must be revised, and has identified a direct link between urban development and the development of bathing culture: key points in the city’s development such as the transformation into a Roman colony in 80 BC and particularly the connection to the Serino aqueduct in the early Imperial period directly impacted on the baths studied – positively in the case of the Stabian Baths, negatively in the case of the Republican Baths.
REPORTS (pdf)
- Report of the March 2023 Season. Stabian Baths
- Report of the June 2022 Season. Stabian Baths
- Report of the September 2021 Season. Stabian Baths
- Report of the March 2019 Season. Stabian and Republican Baths
- Report of the March 2018 Season. Stabian Baths
- Report of the March 2017 Season. Stabian Baths
- Report of the September 2016 Season. Republican Baths
- Report of the March 2016 season. Stabian Baths
- Report of the September 2015 Season. Republican Baths
RESEARCH TEAM (2015-2024)
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Clemens Brünenberg; Fachbereich Architektur, Fachgebiet Klassische Archäologie, Technische Universität Darmstadt
- Prof. Dr. Jens-Arne Dickmann, Institut für Archäologische Wissenschaften, Klassische Archäologie, Universität Freiburg
- Dr. Domenico Esposito, Institut für Klassische Archäologie, FU Berlin
- Dr. Antonio Ferrandes, Facoltà di Lettere e Filosofia, Sapienza Università di Roma
- Dr. Marco Giglio, Dipartimento Asia Africa e Mediterraneo, Università degli Studi di Napoli L’Orientale
- Dr. des. Thomas Heide, Institut für Altertumswissenschaften, Klassische Archäologie, Johannes Gutenberg Universität Mainz
- Prof. Dr. Dominik Lengyel, Architektur und Visualisierung, Brandenburgische Technische Universität Cottbus-Senftenberg
- Dr. Asja Müller, Institut für Klassische Archäologie, FU Berlin
- Prof. Dr. Giacomo Pardini, Dipartimento di Scienze del Patrimonio Culturale/DISPAC, Università degli Studi di Salerno
- Prof. emeritus Dr. Cees Passchier, Institut für Geowissenschaften, Universität Mainz
- Dr. Alessandra Pegurri, Facoltà di Lettere e Filosofia, Sapienza Università di Roma
- Prof. emeritus Dr. Mark Robinson, Environmental Archaeology, University of Oxford
- Jennifer Robinson, Environmental Archaeology, Oxford
- Dr. Christoph Rummel, Römisch-Germanische Kommission, Frankfurt am Main
- Martin Strauß, MA Student, Wasserbau/ Ingenieurswissenschaften, Technische Hochschule Lübeck
- Dr. Gül Sürmelihindi, Institut für Geowissenschaften, Universität Mainz
- Catherine Toulouse, Selbständige Architektin
- Prof. Dr. Monika Trümper, Institut für Klassische Archäologie, FU Berlin
- Dr. Kai Wellbrock, Wasserbau/ Ingenieurswissenschaften, Technische Hochschule Lübeck
PUBLICATIONS
Brünenberg, C. – C. Rummel – M. Trümper, Use and Application of SfM-based Documentation in Excavation and Standing Remains Assessment of the Stabian Baths, Pompeii, in: Proceedings of Conference the European Association of Archaeologists 2019, Bern (2024)
Esposito, D., Decorative Principles Between the Public and Private Sphere in Pompeii, in: A. Haug – T. Lauritsen (eds.), Principles of Decoration in the Roman World (Berlin 2021) 53–69
Heide, T., Der Brunnen der Republikanischen Thermen in Pompeji. Architektonische Analyse und Rekonstruktion des antiken Wasserhebemechanismus, RM 127, 2021, 221–253
Heide, T., Public Deep Wells of Pompeii: Processes of Construction, in: D. Maschek – M. Trümper (eds.), Architecture and the Ancient Economy (Rome 2022) 173–190
Heide, T., Wasserbewirtschaftung öffentlicher Badeanlagen in den Vesuvstädten. Bauhistorische und hydrotechnische Untersuchungen an den Republikanischen Thermen, den Stabianer Thermen sowie den Forumsthermen von Pompeji und Herculaneum, Dissertation Freie Universität Berlin 2023
Henzel, R. – M. Trümper, Crowded or Empty Spaces? The Statuary Decoration of the ‘Palaestrae’ in Pompeii and Herculaneum, in: U. Mania – M. Trümper (eds.), Development of Gymnasia and Graeco-Roman Cityscapes (Berlin 2018) 115–142
Robinson, M. – M. Trümper – C. Brünenberg – J.-A. Dickmann – D. Esposito – A. F. Ferrandes – G. Pardini – A. Pegurri – C. Rummel, Stabian Baths Pompeii: New Research on the Altstadt Defenses, AA 2020, 83–119
Trümper, M., South Baths at Morgantina: Assessment of the Heating System in the Context of Graeco-Roman Public Baths, in: L. Maniscalco (ed.), Morgantina Duemilaquindici. La ricerca archeologica a sessant’anni dall’avvio degli scavi (Palermo 2015) 102-114
Trümper, M., Curare se stessi. Bagni e terme a Pompei, in: M. Osanna – C. Rescigno (eds.), Pompei e i Greci (Milano 2017) 262–267
Trümper, M., Water Management of the Stabian Baths at Pompeii: A Reassessment, in: G. Wiplinger (ed.), Wasserwesen zur Zeit des Frontinus. Bauwerke – Technik – Kultur, Frontinus Symposion Trier Mai 2016 (Leuven 2017) 257–272
Trümper, M., Gymnasium, Palaestra, Campus and Bathing in Late Hellenistic Pompeii: A Reassessment of the Urban Context of the Republican Baths (VIII 5, 36), in: U. Mania – M. Trümper (eds.), Development of Gymnasia and Graeco-Roman Cityscapes (Berlin 2018) 87–113
Trümper, M., Development of Bathing Culture in Hellenistic Sicily, in: M. Trümper – G. Adornato – Th. Lappi (eds.), Cityscapes of Hellenistic Sicily (Rome 2019) 347–391
Trümper, M. – C. Brünenberg – J.-A. Dickmann – D. Esposito – A. F. Ferrandes – G. Pardini – A. Pegurri – M. Robinson – C. Rummel, Stabian Baths in Pompeii: New Research on the Development of Ancient Bathing Culture, RM 125, 2019, 1–56
Trümper, M., Logistics of Building Processes: the Stabian Baths in Pompeii, in: C. Recko – M. Heinzelmann (eds.), Quantifying Ancient Building Economy. Part 3.24 of the 19th International Congress of Classical Archaeology, Cologne/Bonn, May 2018 (Heidelberg 2020) 5–18
Trümper, M., Republican Baths to Casa della Calce. A Radical Transformation Process in Pompeii, in: K. Piesker - U. Wulf-Rheidt [†] (eds.), Umgebaut. Umbau-, Umnutzungs- und Umwertungsprozesse in der antiken Architektur. DiskAB 13 (Regensburg 2020) 11–28
Trümper, M., Water Management of Late Republican Baths, in: S. Bouffier – I. Fumadó Ortega (eds.), L'eau dans tous ses états. Perceptions antiques (Aix-en-Provence 2020) 141–159
Trümper, M., Late Republican Baths in Italy: Urban Context and Ownership, RM 128, 2022, 268–335
Trümper, M. – D. Esposito, Le Terme Stabiane dopo il terremoto del 62 d.C., in: H. Dessales (ed.), Ricostruire dopo un terremoto. Riparazioni antiche a Pompei (Naples 2022) 221–242
Trümper, M. – C. Brünenberg – D. Esposito – Th. Heide – K. Zielke, The Men’s Tepidarium of the Stabian Baths at Pompeii: Quantification of its Construction and Remodeling Processes, in: D. Maschek – M. Trümper (eds.), Architecture and the Ancient Economy (Rome 2022) 219–256
Trümper, M. – M. Giglio – M. Robinson – A. Ferrandes – G. Pardini – A. Pegurri, Pompei Terme Stabiane: Campagna di 2021, Rapporto preliminare, Rivista di Studi Pompeiani 33, 2022, 200–207
Trümper, M. – M. Giglio – A. Ferrandes –A. Pegurri, Stabian Baths at Pompeii. Preliminary Report of the 2022 Campaign, Rivista di Studi Pompeiani 34, 2023
Trümper, M., Baths and Bathing in Pompeii, in: J. Berry – R. Benefiel (eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Pompeii and Environs (Oxford 2024)
Trümper, M. – M. Giglio – A. Müller – M. Robinson, Public Saunas in the Stabian Baths – A Privilege of Men, E-Journal degli Scavi di Pompei 2024
Trümper, M. – D. Esposito – C. Brünenberg –A. Ferrandes – G. Pardini – A. Pegurri M. Robinson, Republican Baths at Pompeii. New Research on the Development and Function (submitted for review)
FASTI ONLINE REPORTS
Republican Baths
Fasti Online: Pompeii, Republican Baths (VIII 5, 36)
- Fasti OnLine - Season 2015.pdf
- Fasti OnLine - Season 2016.pdf
- Fasti OnLine - Season 2019.pdf
- Plan Trenches 2015-2019.pdf
Stabian Baths
Fasti Online: Pompeii, Stabian Baths (VII 1, 8)
- Fasti OnLine - Season 2015.pdf
- Fasti OnLine - Season 2016.pdf
- Fasti OnLine - Season 2017.pdf
- Fasti OnLine - Season 2018.pdf
- Fasti OnLine - Season 2021.pdf
- Fasti OnLine - Season 2022.pdf
- Fasti OnLine - Season 2023.pdf
- Plan Trenches 2016-2023.pdf
PUBLIC OUTREACH
ZDF Terra X Verlorenes Wissen: Sonnenpillen und Superbeton der Antike; 30.6.2019; https://www.zdf.de/dokumentation/terra-x/verlorenes-wissen-mit-harald-lesch-sonnenpillen-und-der-superbeton-der-antike-100.html
Forschergeist FG041 Klassische Archäologie; Podcast: Interview des Water and Bathing, Archaeology magazine July/August 2019; https://www.archaeology.org/issues/344-1907/features/7717-pompeii-water-bathing
Stifterverbandes mit Monika Trümper; Dezember 2016; https://fyyd.de/episode/1499194
Der mannigfaltigste Lärm umrauscht mich von allen Seiten: Fundiert, Wissenschaftsmagazin der FU Berlin, 13.10.2016; https://www.fu-berlin.de/presse/publikationen/fundiert/2016_01/10-baeder/index.html
Antike Badefreuden: Tagesspiegel-Beilage, 23.9.2016; https://www.fu-berlin.de/presse/
publikationen/ tsp/2016/tsp-september-2016/forschung/antike-badefreuden/index.html
Hidden Secrets of Pompeii: National Geography Feature, 2021/2022
Press Comments on Discovery of a Turtle in 2022
- https://www.storicang.it/a/scoperti-i-resti-di-tartaruga-a-pompei_15638
- https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-61931172
- https://www.spiegel.de/wissenschaft/natur/forscher-graben-fast-2000-jahre-alte-schildkroete-in-pompeji-aus-sie-starb-weil-sie-kein-ei-legen-wollte-a-d9662957-63f3-4c11-8c73-70b88a620432
- http://pompeiisites.org/comunicati/pompei-un-laboratorio-permanente-di-studio-e-ricerca/
- http://pompeiisites.org/comunicati/il-ritrovamento-di-una-testuggine-di-2000-anni-fa-e-del-suo-uovo/
- https://www.rainews.it/articoli/2022/06/nuova-scoperta-a-pompei-dagli-scavi-una-tartaruga-col-suo-uovo-intatta-dopo-2mila-anni-7e91f50d-ac8c-4e0c-a602-f03b97d3fef8.html
- https://www.corriere.it/cronache/22_giugno_24/pompei-tartaruga-ritrovata-scavi-dc60590a-f3aa-11ec-b4bb-7eb5df080865.shtml
- https://www.arte.it/notizie/napoli/un-insolito-ritrovamento-getta-nuova-luce-sulla-storia-di-pompei-19493
Press Comments on Discovery of Mosaic floors in 2023
- https://napoli.repubblica.it/cronaca/2023/03/20/news/pompei_un_laboratorio_permanente_di_studio_e_ricerca-392957980/
- https://www.rainews.it/articoli/ultimora/Pompei-sotto-Terme-pavimento-a-mosaico-d2b9626c-e06b-4d9d-95e0-a8d126d1bb75.html